我们可以通过CSS注入来使得浏览器加载需要的字体文件, 以JetBrains Mono为例
详细步骤
准备字体文件
从JetBrains Mono官网下载字体文件,并把woff和woff2格式的字体文件放置在fonts目录,并把fonts目录移到code-server安装路径下的 lib/vscode/out/vs/code/browser/workbench 位置。
以下是目录树
/usr/lib/code-server/lib/vscode/out/vs/code/browser/workbench
├── fonts
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Bold-Italic.woff
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Bold-Italic.woff2
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Bold.woff
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Bold.woff2
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-ExtraBold-Italic.woff
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-ExtraBold-Italic.woff2
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-ExtraBold.woff
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-ExtraBold.woff2
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Italic.woff
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Italic.woff2
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Medium-Italic.woff
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Medium-Italic.woff2
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Medium.woff
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Medium.woff2
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Regular.woff
│ └── JetBrainsMono-Regular.woff2创建css文件
新建一个 fonts.css 放在code-server安装路径下的 lib/vscode/out/vs/code/browser/workbench 位置
我的是 /usr/lib/code-server/lib/vscode/out/vs/code/browser/workbench
@font-face {
font-family: 'JetBrains Mono';
src: url('fonts/JetBrainsMono-Regular.woff2') format('woff2'),
url('fonts/JetBrainsMono-Regular.woff') format('woff');
font-weight: 400;
font-style: normal;
}
@font-face {
font-family: 'JetBrains Mono';
src: url('fonts/JetBrainsMono-Italic.woff2') format('woff2'),
url('fonts/JetBrainsMono-Italic.woff') format('woff');
font-weight: 400;
font-style: italic;
}
/* 可根据需要添加更多字重和样式 */
/*
@font-face {
font-family: 'JetBrains Mono';
src: url('fonts/JetBrainsMono-Medium.woff2') format('woff2'),
url('fonts/JetBrainsMono-Medium.woff') format('woff');
font-weight: 500;
font-style: normal;
}
@font-face {
font-family: 'JetBrains Mono';
src: url('fonts/JetBrainsMono-Medium-Italic.woff2') format('woff2'),
url('fonts/JetBrainsMono-Medium-Italic.woff') format('woff');
font-weight: 500;
font-style: italic;
}
@font-face {
font-family: 'JetBrains Mono';
src: url('fonts/JetBrainsMono-Bold.woff2') format('woff2'),
url('fonts/JetBrainsMono-Bold.woff') format('woff');
font-weight: 700;
font-style: normal;
}
@font-face {
font-family: 'JetBrains Mono';
src: url('fonts/JetBrainsMono-Bold-Italic.woff2') format('woff2'),
url('fonts/JetBrainsMono-Bold-Italic.woff') format('woff');
font-weight: 700;
font-style: italic;
}
@font-face {
font-family: 'JetBrains Mono';
src: url('fonts/JetBrainsMono-ExtraBold.woff2') format('woff2'),
url('fonts/JetBrainsMono-ExtraBold.woff') format('woff');
font-weight: 800;
font-style: normal;
}
@font-face {
font-family: 'JetBrains Mono';
src: url('fonts/JetBrainsMono-ExtraBold-Italic.woff2') format('woff2'),
url('fonts/JetBrainsMono-ExtraBold-Italic.woff') format('woff');
font-weight: 800;
font-style: italic;
} */修改 workbench.html
编辑工作台 HTML 文件,在 <head> 部分添加 CSS 引用:
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{{WORKBENCH_WEB_BASE_URL}}/out/vs/code/browser/workbench/fonts.css">最终目录结构
没有用到的字体可以不放
/usr/lib/code-server/lib/vscode/out/vs/code/browser/workbench
├── callback.html
├── fonts
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Bold-Italic.woff
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Bold-Italic.woff2
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Bold.woff
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Bold.woff2
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-ExtraBold-Italic.woff
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-ExtraBold-Italic.woff2
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-ExtraBold.woff
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-ExtraBold.woff2
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Italic.woff
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Italic.woff2
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Medium-Italic.woff
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Medium-Italic.woff2
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Medium.woff
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Medium.woff2
│ ├── JetBrainsMono-Regular.woff
│ └── JetBrainsMono-Regular.woff2
├── fonts.css
├── workbench.css
├── workbench.html
├── workbench.js
└── workbench.js.map设置编辑器字体
修改setting.json的相关内容
{
"editor.fontFamily": "'JetBrains Mono', Consolas, 'Courier New'",
"editor.fontLigatures": true, //对于连字字体,一定要打开连字符功能
}注意: 对于连字字体,一定要打开fontLigatures 否则会出现光标错位问题
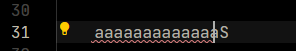
此时,我的光标所在位置应该是行末
最后效果